Let’s start to unpack what happened in that experiment.
Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells. During this process, plants take in sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen.
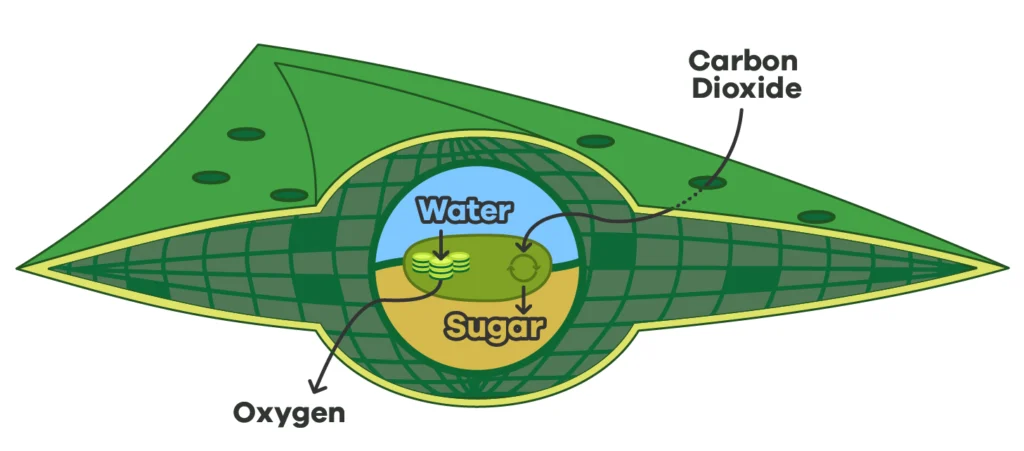
Chlorophyll, a green pigment found in chloroplasts, is crucial because it absorbs the sunlight needed for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll is especially good at absorbing red and blue wavelengths of light (see absorption spectrum)! Red light is considered more efficient for photosynthesis because it is lower energy. No energy gets wasted!
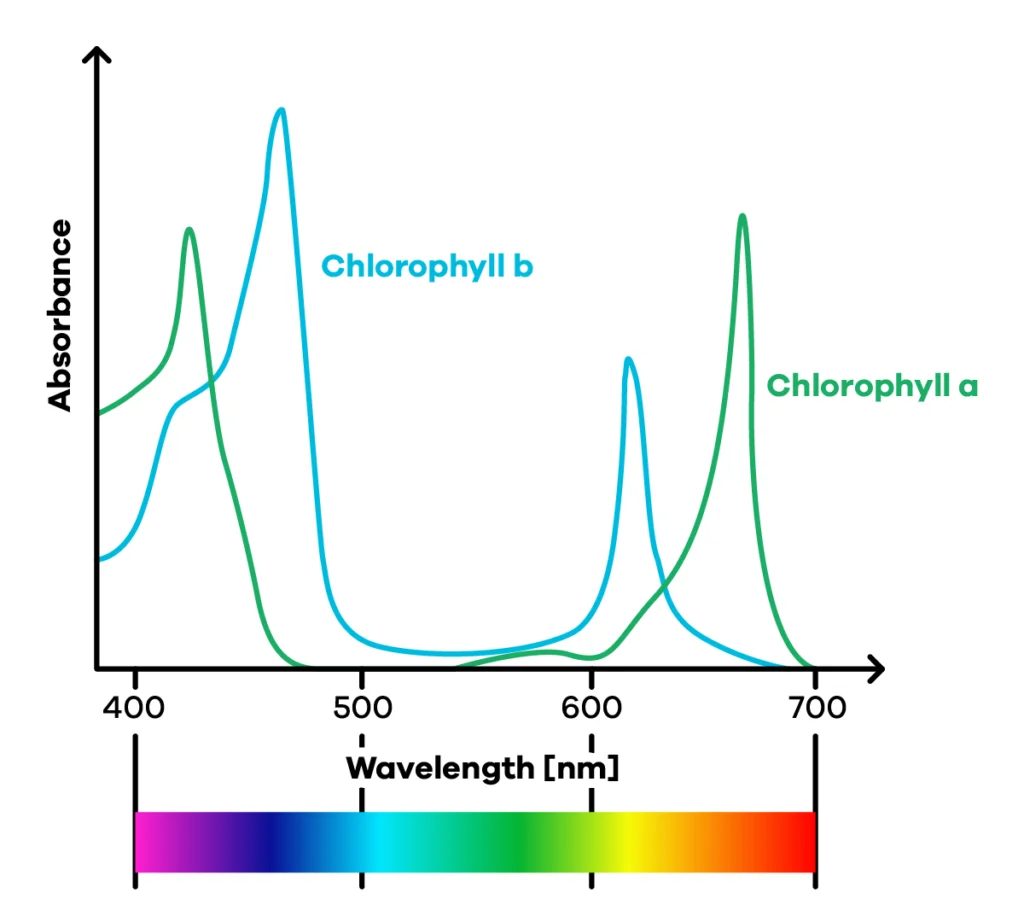
Still, as we’ve seen, normal plant growth requires red and blue light. Why? Well, plants need blue light for the:
- development and movement of chloroplasts within plant cells
- production of chlorophyll
- regulation of stomatal opening, which is essential for gas exchange
- growth towards light sources
THINK-PAIR-SHARE
While red light is most efficient for photosynthesis, some level of blue light is essential.
How does blue light contribute to a plant’s ability to photosynthesize?
Without blue light, plants could not produce chloroplasts or chlorophyll or regulate gas exchange through the stomata. All of these things are essential for photosynthesis.
Additionally, blue light allows plants to change their structure in response to the light in their environment. They can grow towards light or move their chloroplasts to positions that maximize light absorption. This maximizes photosynthesis.